
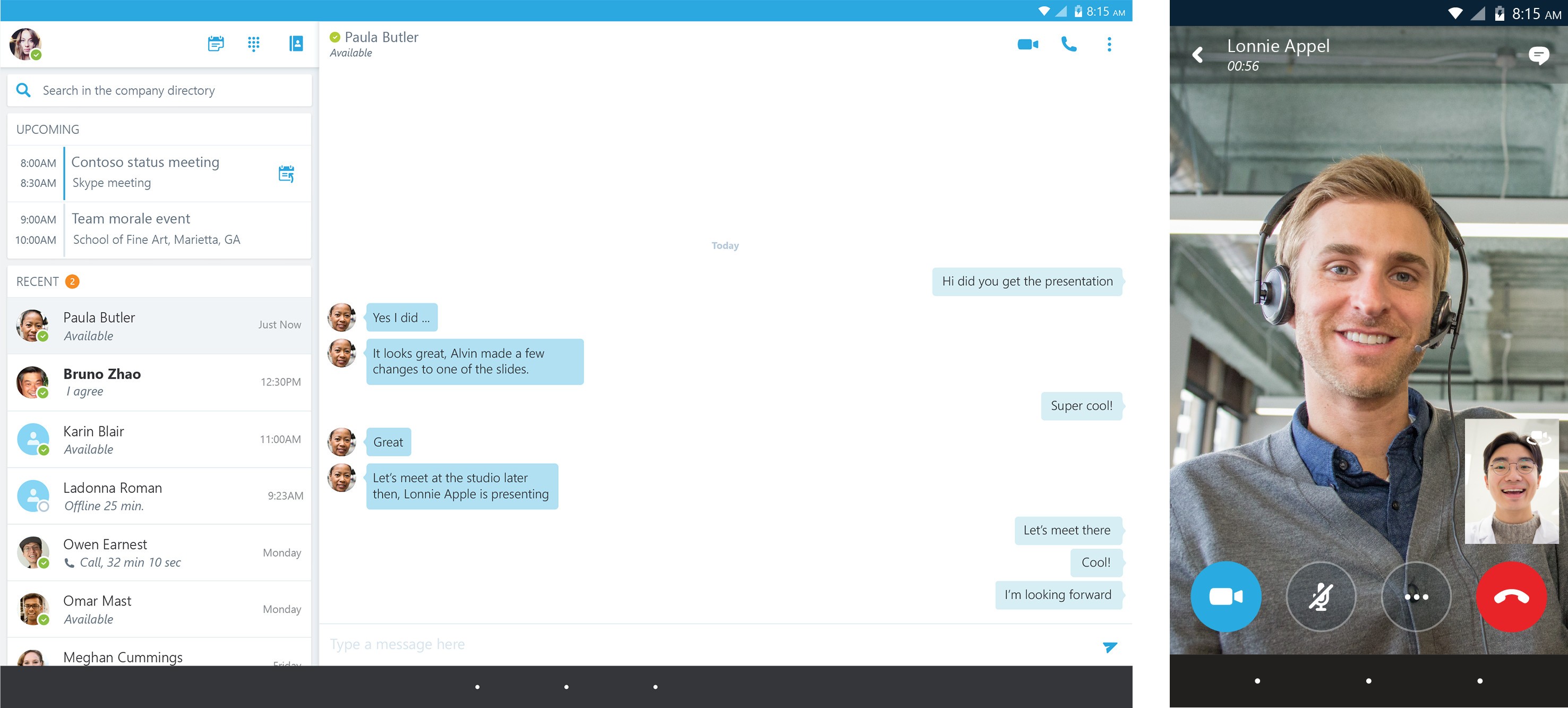
Subsequent packets will be dropped by the SRX, since they do not match an existing flow session anymore (and they cannot establish a new flow session, since these are not TCP SYN packets).However, approximately 2 seconds later, the invalidation timer expires, and the flow session gets invalidated on the SRX.The communication between the client and the Edge Server starts. The packet reaches the Edge Server successfully, TCP 3-way Handshake continues, and the flow session gets eventually established.It matches exactly the same pending flow session, since the entire 5-tupple (src/dst IP, src/dst port, protocol) matches it. In the meantime, the client sends the second TCP SYN packet.The SRX starts the above mentioned invalidation timer.
The Edge Server responds with TCP RST.A pending flow session is created on the SRX. The first TCP SYN passes through the SRX and successfully reaches the Edge Server.In the described case, the following occurs: The default behavior on the SRX is to maintain a special invalidation timer that postpones session invalidation by approximately 2 seconds after the receiving of TCP RST. Notice the second TCP SYN uses exactly the same source and destination port numbers and is sent almost immediately after the first attempt. This is demonstrated in the following packet capture by the tcpdump tool on the Edge Server: # First SYNġ6:07:40.301524 IP (tos 0x0, ttl 64, id 0, offset 0, flags, proto TCP (6), length 60)Ģ0.1. Eventually, the TCP SYN will be accepted by the Edge Server, and the normal TCP 3-way handshake will continue (this will happen once the authentication is completed). The client will then retry the connection, using exactly the same TCP source/destination ports. However, an important detail is that the Edge Server will reject the client's attempts to establish a TCP connection until the client finishes the authentication procedure.Īs a result, the Edge Server might respond with TCP RST flag to a TCP SYN packet sent by the client (this happens when the authentication is still in progress). The details of this implementation are beyond the scope of this article. The authentication is done in parallel, via a service called MRAS (Media Relay Authentication). However, in order for this connection to be accepted, the clients must be first authenticated. This issue is related to the way Microsoft Skype for Business clients communicate to Microsoft A/V Edge Server.Ī client establishes a TCP connection to the Edge Server, using dynamically chosen TCP ports.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
